Andrea CITRINI, Adriano MAYER, Corrado CAMERA, Anita EROSS, Jürgen SULTENFUß, Guido PEZZERA, & Giovanni Pietro BERETTA (2024)
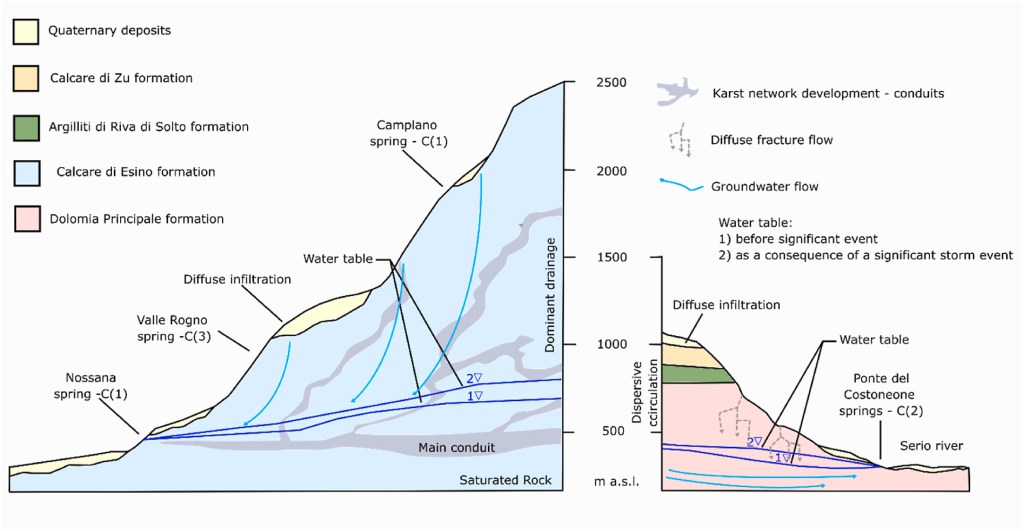
This study focuses on the hydrogeochemical and isotopic characterization of the two main karst aquifers in the Middle Valseriana Valley (Northern Italy): Nossana and Ponte del Costone springs, which supply drinking water to approximately 500,000 people. The goal is to better understand the internal dynamics of these systems using chemical analysis, stable isotopes, and ³H/³He dating, establishing a baseline for future monitoring in the context of climate change.
∇ – Methods
The study followed a three-part approach:
- Water Sampling Campaign
- 34 water points (springs, rivers, wells, caves, mines) were sampled from 2018–2019.
- Tritium-Helium (³H/³He) dating was performed in 2015 and 2019 at 5 selected springs.
- Hydrochemical and Cluster Analysis
- Major ions (Ca²⁺, Mg²⁺, HCO₃⁻, SO₄²⁻, etc.) were measured.
- A hierarchical clustering defined 3 groups of springs based on elevation and chemistry.
- ³H/³He Age Dating
- Calculated groundwater residence times and recharge altitudes.
- Corrected for excess air and radiogenic helium (⁴He).
∇ – Main Results
- Three Spring Classes Identified:
- C(1): High-altitude springs – very young waters (<1 year), low noble gas excess.
- C(3): Mid-altitude springs – intermediate ages (4–7 years).
- C(2): Valley-bottom springs – oldest waters (up to 32 years), high ⁴He and sulfate levels.
- Feasibility of ³H/³He Dating in Karst Systems:
- Demonstrated successful use of the method with careful sampling, even in complex karst settings.
- Reproducible results between 2015 and 2019.
- Evidence of Recent System Changes:
- Increase in groundwater ages between 2015 and 2019 suggests lower recharge altitudes, possibly due to decreasing snowfall or winter recharge.
∇ – Conclusion
The study provides a conceptual model of the two karst systems, revealing:
- Strategic importance of the springs for regional water supply.
- C(2) valley springs are more vulnerable and should be prioritized for protection.
- Nossana spring, while chemically similar to high-altitude springs, shows longer flow paths and intermediate residence times — critical for regional supply and must be safeguarded.
- The ³H/³He method is validated for tracking groundwater renewal cycles.
- Between 2015 and 2019, the system shows aging waters and reduced recharge renewal, underscoring the need for long-term monitoring under climate change scenarios.
∇ – Resources
Citrini, A., Mayer, A., Camera, C. A., Erőss, A., Sültenfuß, J., Pezzera, G., & Beretta, G. P. (2024). Hydrogeochemical and isotopic characterization of the main karst aquifers of the middle Valseriana (Northern Italy): Nossana and Ponte del Costone springs. Applied Geochemistry, 169, 106046.
Leave a comment